Describe the Organization of the Eukaryotic Chromosome.
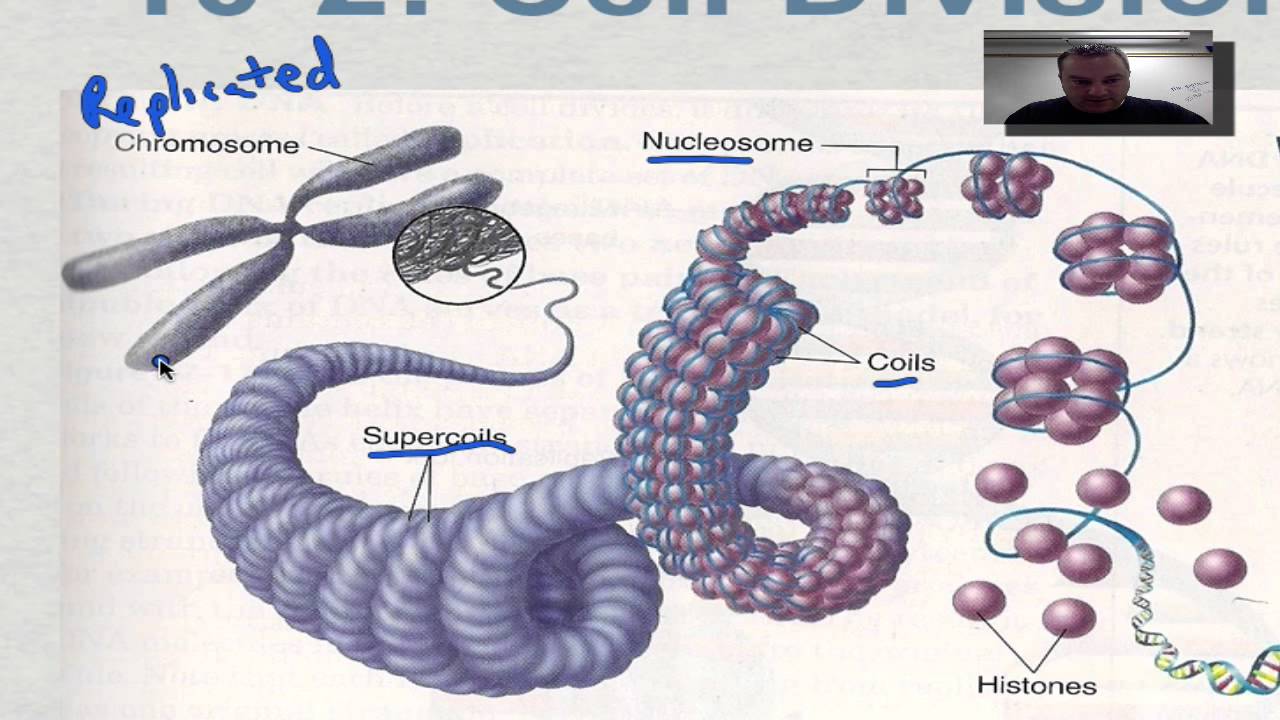
The DNA is wound around proteins called histones. The histones then stack together in a.
Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure Overview Youtube
9 - Transcribe and translate the following DNA.

. Three levels of structural organization of eukaryotic DNA in the cell nucleus are considered in this paper. The role these highly condensed chromosomes is to organize and package the giant DNA molecules of eukaryotic chromosomes into structures that will facilitate their seggregation to daughter nuclei without the DNA molecules of different chromosomes. At the time of mitosismeiosis nucleus coils the chromosomes and duplicates them-making a set of brains for the daughter cell.
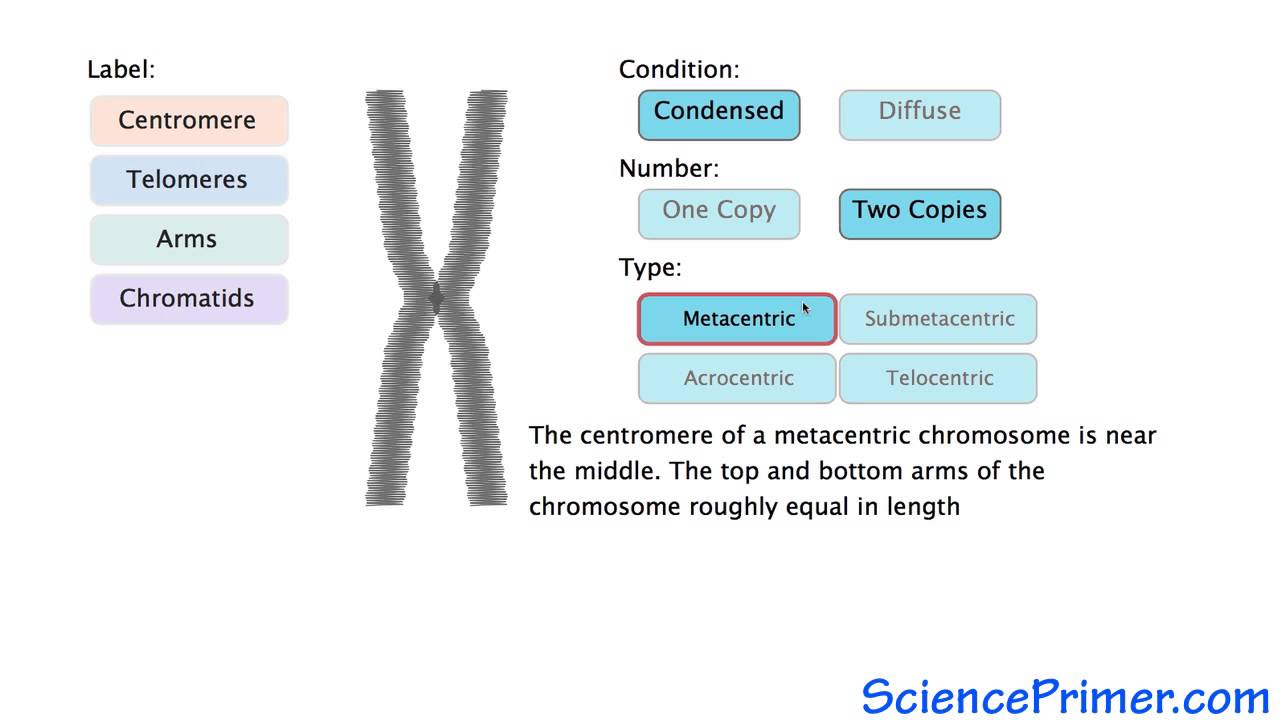
The following illustration explores the shape classification and features of a eukaryotic chromosome. Describe eukaryotic genes. Chromosomes contain long strands of DNA containing genetic information.
Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus where it is called nuclear DNA but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria. The tight coiling and high degree of organization in this supercoiled DNA facilitate proper segregation during mitosis and cell division. Outline Introduction General features of eukaryotic genomes and chromosomes C value paradox.
Regulatory regions of eukaryotic chromosomes Databases of regulatory factors. Carries heridtary information- information that determine what kind of cell it is- as genes in chromosomes. Chromosomes are condensed chains of DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
The fundamental unit of chromatin is. Eukaryotic chromosomes are much larger in size and requires special proteins called histone proteins which forms a special structure called nucleosomes when DNA is wrapped. Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of a DNA-protein complex that is organized in a compact manner which permits the large amount of DNA to be stored in the nucleus of the cell.
Describe the organization of the eukaryotic chromosome. Genome browsers Analysis of chromosomes using BioMart and biomaRt. 9 - Describe the structure and complementary base.
The subunit designation of the chromosome is chromatin. This problem has been solved. The fundamental unit of chromatin is the nucleosome.
The Chromatin and. And contrast methods to measure chromosomal change. During cell division eukaryotic chromosomes condense into highly coiled structures.
Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. 9 - Describe the organization of the eukaryotic. The subunit designation of the chromosome is chromatin.
9 - Describe how. The whole DNA in our nucleus is assembled into number of chromosomes. Describe the general organization of a eukaryotic chromosome.
Iii the mode of suprasolenoidal DNP-packing--loops or domains. METAPHASE Metaphase chromosomes are the most condensed of normal eukaryotic chromosome. Solution for Describe the organization of the eukaryotic chromosome.
Each chromosome contains a molecule of DNA that is wound tightly around clusters of histone proteins. The whole DNA in our nucleus is assembled into number of chromosomes. Eukaryotic chromosome structure refers to the levels of packaging from raw DNA molecules to the chromosomal structures seen during metaphase in mitosis or meiosis.
Compared to prokaryotic chromosomes eukaryotic chromosomes are much larger in size and are linear chromosomes. For all of this DNA to fit into the nucleus tremendous packing and folding are required The chromosomes are in an elongated relatively The chromosomes are in an elongated relatively. The DNA is naked and is not associated with histone proteins.
In order for the chromosome to fit into the microscopic nucleus eukaryotic chromosomes have developed a mechanism to condense and organize the DNA into structures called chromosomes. The basic terminology for chromosomes is chromatin. Describe the organization of the eukaryotic chromosome.
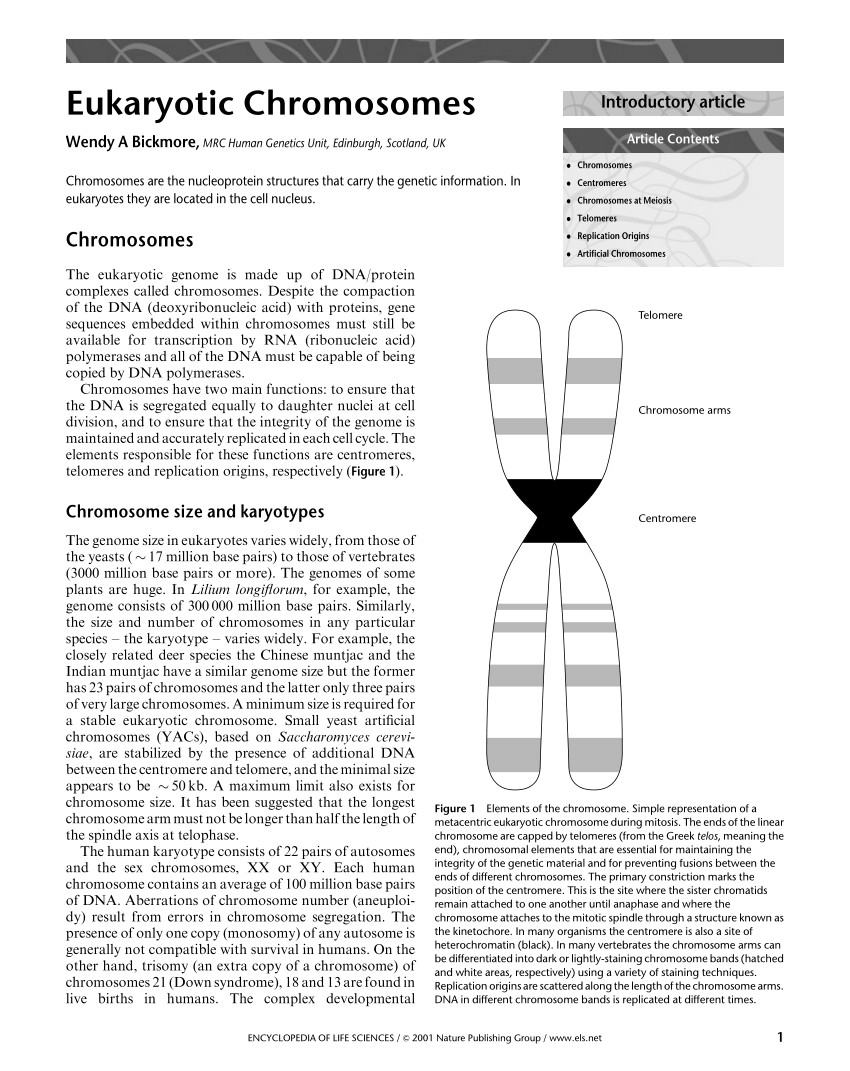
It is circular in shape and attached to the plasma membrane by an in folding called the mesosome. Organization of Eukaryotic Chromosomes Each eukaryotic chromosome consists of a single extremely long molecule of DNA. The DNA inside the nucleus is organized into chromosomes.
Start your trial now. Organization of Eukaryotic Chromosomes A eukaryotic chromosome contains a long linear DNA molecule Three types of DNA sequences are required for chromosomal replication and segregation Origins of replication Centromeres Telomeres. Eukaryotic cells have multiple chromosomes that are linear in shape.
The nucleus divides into two segments- effetively dividing the generic material. Eukaryotic chromosomes are made up of a compacted DNA-protein complex that allows the cell nucleus to retain a substantial amount of DNA. At the most basic level a chromosome is a molecule of DNA that is tightly coiled around proteins called histones.
Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms carrying the genetic information in genes. The chromosome consists of a double stranded helix of DNA. First week only 499.
The nucleosome is the most fundamental component of chromatin. However small amounts of protein mainly RNA polymerase is found to be associated with it. I the chain of nucleosomes.
The packaging of the chromosome in prokaryotic cell is rather simpler then the eukaryotic cell. Describe the general organization of a eukaryotic chromosome. Prokaryotic chromosome is packed with the help of nucleoid associated proteins which helps in packaging.
Ii the solenoidal or superbead nucleomere model of compactization of the nucleosomal fiber. Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of a DNA-protein complex that is organized in a compact manner which permits the large amount of DNA to be stored in the nucleus of the cell. 9 - How do the linear chromosomes in eukaryotes ensure.
Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of a DNA-protein complex that is organized in a compact manner which permits the large amount of DNA to be stored in the nucleus of the cell.

6 5 Eukaryotic Chromosomal Structure And Compaction Chemistry Libretexts
No comments for "Describe the Organization of the Eukaryotic Chromosome."
Post a Comment